POS 22 vs POS 11: Key Differences, Correct Usage and Reimbursement Rules

BLOG OUTLINE
- Introduction
- Facility vs Non-Facility POS Codes
- Understanding the difference between POS 22 and POS 11
- Importance of POS 22 and Other One in Healthcare Facilities
- Coding Errors with POS 22
- Billing Guidelines for correct use of POS 22 Vs. The Other
- Training Staff on Proper POS 22 and 11 Coding
- Impact of applying POS 22 Vs. 11 on Reimbursement Rates
Introduction
In medical billing, every claim must specify the place of service (POS) — the setting where care was delivered. Two of the most frequently used and often confused codes are POS 11 (Office) and POS 22 (On-Campus Outpatient Hospital).
Understanding how these two differ is critical for accurate claims submission, compliance with payer rules, and preventing costly denials. This guide explains what each code means, when to use them, and how choosing between the two impacts reimbursement for your practice.
Related reading: Explicit details on Place of Service 11
For Insurance Credentialing, Medical Billing Services and other services
Facility vs Non-Facility POS Codes
In healthcare billing, facility and non-facility POS codes indicate whether services were performed in a hospital or an independent practice.
- Facility settings include hospitals, outpatient departments, and emergency rooms.
- Non-facility settings include physician offices, homes, or independent clinics.
🩺 For detailed comparison on facility vs. non-facility POS codes, see our Complete Guide to Place of Service Codes.
Understanding The Difference Between POS 22 and POS 11
When it comes to the essentials, understanding how these codes differ is critical.
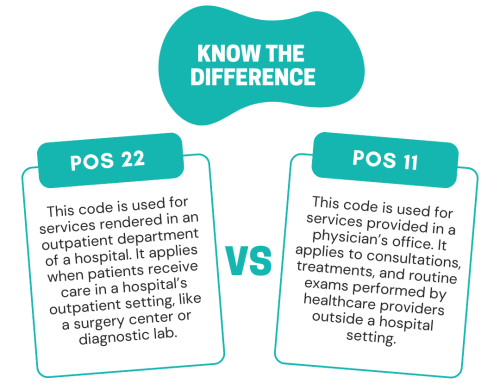
Example to Understand Accurate Use of Both Codes
Example of POS 22: A patient receiving a diagnostic test in a hospital outpatient clinic should be billed with POS 22, indicating a facility-based outpatient service.
Example of POS 11: If that same service happens in a private physician’s office, this code applies.
The difference is not about the procedure, it is about the site of care and who bears the cost of facility resources.
Using the wrong POS can cause underpayment or payer recoupments
Importance of POS 22 and Other One in Healthcare Facilities
Assigning the correct Place of Service (POS) code is more than a technical step — it directly affects reimbursement accuracy and compliance. Each code tells the payer where the care was delivered and determines whether facility or non-facility rates apply.
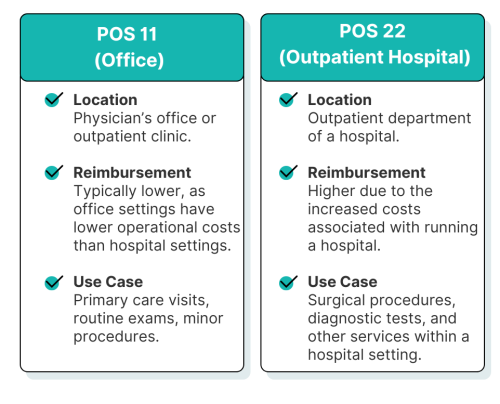
POS 22 (On-Campus Outpatient Hospital)
Identifies services performed in a hospital’s outpatient department.
This helps hospitals recover the higher overhead costs associated with specialized equipment, nursing staff, and facility maintenance.POS 11 (Physician’s Office)
Represents professional services rendered in a private or group practice.
These claims usually qualify for the non-facility rate, reflecting the lower operating costs of independent offices.
Even a small coding error between the two codes can result in:
Delayed payments if the claim is flagged for review.
Under-payment when the payer reimburses at the wrong rate.
Compliance risk if documentation doesn’t match the reported site of care.
Tip: Always align your documentation, credentialing, and claim forms with the physical location of the service. This ensures both compliance and timely reimbursement.
Coding Errors With POS 22
Even experienced billing teams sometimes confuse how to apply Place of Service (POS) codes — especially when outpatient and office settings overlap. Here are some of the most frequent misconceptions and how to correct them
Mixing Up Outpatient and Office Visits
It’s easy to assume all non-inpatient services use the same code.
In reality, a hospital outpatient clinic requires POS 22, while an independent physician office requires the other.
Using the wrong code can change reimbursement rates and create documentation mismatches that trigger audits
Assuming POS 22 Always Results in Higher Reimbursement
Many providers think hospital-based claims automatically pay higher.
However, payer contracts may reimburse professional components at a lower rate when POS 22 is used, since a separate facility fee goes to the hospital.
The correct approach is to match the site of care — not chase the higher rate
Using POS 11 for Every Office Visit
Not all office-like encounters qualify for this location code.
For example, telehealth sessions require their own designated telehealth POS codes and modifiers.
Always verify that the reported POS truly reflects where and how care occurred.
Ignoring Payer-Specific Definitions
Commercial payers and Medicare sometimes differ in how they define outpatient vs. office locations.
Always review the payer’s POS documentation, especially if your practice operates both a hospital-based clinic and a private office
⚠️ Pro Tip: Build an internal cheat sheet showing examples of POS 22 claims and others. Regular training reduces denials and ensures consistent claim documentation across providers
Billing Guidelines for Correct Use of POS 22 VS The Other
Selecting the right Place of Service (POS) code starts with verifying where and how a service was provided. Incorrect selection can cause claim rejections, payer audits, or reimbursement discrepancies — especially when both hospital and office settings are involved. Follow these essential billing steps to stay compliant and accurate.
✅ 1️⃣ Verify the Service Location
Before submitting any claim, confirm the exact location where the provider rendered care:
- Use POS 11 when services occur in a physician’s office or non-hospital setting.
- Use POS 22 when services are provided in an on-campus outpatient hospital department.
- If your organization operates both, cross-check which Tax ID or NPI is associated with each site to ensure consistency.
✅ 2️⃣ Review Payer-Specific Rules
Each payer — including Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial insurers — may define outpatient and office differently.
For example:
- Some payers reimburse telehealth visits under POS 10 or POS 02.
- Certain Medicaid programs require additional modifiers for outpatient claims using POS 22.
🏥 Always consult your payer’s latest provider manual before claim submission
✅ 3️⃣ Align Documentation With POS Selection
Ensure the service documentation clearly describes:
- The physical site of service
- The ownership of the facility (hospital-affiliated vs independent)
- The supervising provider and equipment used
If the claim indicates POS 22 but notes “performed in private office,” auditors can flag the discrepancy
✅ 4️⃣ Verify Claim Forms
- CMS-1500 → Used for professional components in both settings under discussion. Read details on CMS 1500 claim form
- UB-04 → Used by hospital facilities for the facility portion of POS 22 claims. Learn how claims are submitted using UB-04 form
Split-billing scenarios (hospital + physician) require accurate NPI and location data for both entities.
✅ 5️⃣ Conduct Periodic Audits
- Internal audits every quarter help catch location-coding errors early.
- Compare POS codes against EHR location data and scheduling logs to confirm accuracy.
⚡ Pro tip: Integrate your EHR and billing software to auto-assign the correct POS based on service location
Understand how POS and modifiers interact in mental health billing
Training Staff on Proper POS 22 and 11 Coding
A well-trained billing team is your first line of defense against claim errors and revenue loss. Since Place of Service (POS) codes directly determine reimbursement rates, proper staff education ensures every claim reflects the true care setting — minimizing compliance risk and payment delays. Here’s how structured training can strengthen your billing workflow:
Begin by ensuring all staff — from front desk schedulers to billing specialists — understand what each POS code represents.
- POS 11 = Physician’s Office or Independent Practice
- POS 22 = On-Campus Outpatient Hospital Department
When every team member knows how these codes differ, claim data becomes consistent across scheduling, documentation, and billing systems.
Real-world examples help billing teams retain rules better than theory alone. Train coders using sample cases that show when to apply POS 22 Vs. the others:
- Scenario 1: Follow-up visit in a private clinic → POS 11
- Scenario 2: Diagnostic imaging in a hospital outpatient suite → POS 22
- Scenario 3: Telehealth visit (requires POS 10 or POS 02)

Every payer has its own interpretation of facility vs non-facility rules. Include payer policy updates and CMS bulletins in your training sessions to help staff stay current on evolving billing guidelines. See CMS official list of Place of Service codes here
Conduct periodic audits of submitted claims to identify POS-related discrepancies. If errors are discovered, use them as learning opportunities rather than punitive measures. Continuous feedback loops create a culture of accuracy and accountability.
Working with certified billing professionals ensures your internal training aligns with current industry regulations. Outsourcing part of the training or compliance review process to a specialized team like MedStates allows your staff to focus on patient care while maintaining claim accuracy and compliance.

Impact of Applying POS 22 VS 11 on Reimbursement Rates
The choice between POS 11 and POS 22 doesn’t just describe where care was provided — it directly influences how much you’re reimbursed. Each code carries a different payment structure, and even small errors can cause major shifts in total reimbursement. Here’s how they differ financially and operationally:
1️⃣ POS 11 — Physician’s Office (Non-Facility Setting)
- Claims are paid at the non-facility rate, which is typically higher for professional services.
- This rate includes both the provider’s professional work and the office overhead (staff, rent, utilities).
- Because there’s no facility fee, reimbursement is streamlined — the entire amount goes to the provider or group practice.
Example: An evaluation & management (E/M) visit coded under POS 11 may reimburse 10–15% more for the professional component compared to POS 22.
2️⃣ POS 22 — On-Campus Outpatient Hospital (Facility Setting)
POS 22 is billed when the service occurs within a hospital’s outpatient department. In this case, reimbursement is split:
- The provider bills the professional component (CMS-1500 form).
- The hospital bills the facility component (UB-04 form).
This split often results in a lower professional reimbursement, since part of the payment covers hospital facility costs. However, overall reimbursement to the hospital system is higher — reflecting the additional overhead.
3️⃣ Financial Implications
| Aspect | POS — Office | POS 22 — Outpatient Hospital |
|---|---|---|
| Reimbursement Type | Non-facility rate (single payment) | Split professional + facility billing |
| Average Professional Payment | Higher | Lower |
| Facility Fee | Not applicable | Billed separately by hospital |
| Claim Form | CMS-1500 only | CMS-1500 + UB-04 |
| Audit Sensitivity | Low–Moderate | Higher (due to split billing) |
Comparative Analysis: POS 11 Vs POS 22 in Medical Billing
Understanding the difference between outpatient office vs outpatient hospital billing is essential for accurate claim submission, reimbursement optimization, and audit compliance.
| Feature | Physician’s Office | POS 22 — On-Campus Outpatient Hospital |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Independent physician office or private practice where professional services are rendered in a non-hospital setting. | Hospital outpatient facility located on the hospital campus where patients receive diagnostic or treatment services. |
| Typical Setting | Private practice, independent clinic, or physician office not physically on a hospital campus. | Hospital outpatient department physically located on the same campus as the hospital. |
| Reimbursement | Typically higher professional reimbursement (no facility fee), though this varies by payer. | Professional fees may be lower; hospital bills a separate facility fee which increases total reimbursement to the system. |
| Billing Entity | Physician or clinic usually bills the professional component (CMS-1500). | Split billing: provider bills professional fee (CMS-1500) and hospital bills facility charges (UB-04). |
| Common Services | Office visits, routine follow-ups, minor in-office procedures. | Outpatient surgery, advanced diagnostics, specialty clinics, complex procedures requiring hospital resources. |
| Prior Authorization | Depends on payer and service — common for certain procedures/therapies. | Often required for higher-cost outpatient services; verify payer policy. |
| Claim Forms | CMS-1500 for professional services. | CMS-1500 for professional services; UB-04 for facility charges. |
| Impact on Patient Cost | Usually lower out-of-pocket costs (no facility fee) — depends on plan benefits. | Often higher out-of-pocket due to facility fee and separate cost-sharing for hospital services. |
| Example POS Code | 11 | 22 |
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Understanding when and how to use POS 22 can make a significant difference in claim accuracy, compliance, and reimbursement outcomes. These two Place of Service codes may appear similar, but the distinction lies in the site of care — and that distinction drives how each payer calculates payment. Here’s a quick recap of what we covered:
POS 11 (Physician’s Office) is used for services performed in an independent, non-hospital setting. It usually receives a higher professional reimbursement since there’s no separate facility fee.
POS 22 (On-Campus Outpatient Hospital) applies to services rendered in a hospital’s outpatient department, where the claim is split between professional and facility components.
Choosing the correct POS ensures claims reflect the actual service location, helping providers remain compliant, avoid underpayment, and reduce the risk of payer audits.
Training and internal audits play a key role in maintaining billing accuracy — especially for organizations with multiple care locations.
Ultimately, correct POS coding is not just about billing, it is about protecting your revenue integrity. When used properly, POS 11 and POS 22 help payers, providers, and patients maintain a fair and transparent reimbursement system
How MedStates Helps Providers Get It Right
At MedStates, we specialize in helping behavioral health, telehealth, and multi-specialty practices eliminate POS-related billing errors. Our credentialed billing experts:
- Review claims for accurate code application and compliance with payer policies,
- Conduct internal audits to prevent costly denials, and
- Provide tailored training to your team for consistent, compliant billing.
💬 If your practice experiences frequent POS-related denials or confusion between facility and non-facility codes, our billing experts can help streamline your process — from claim submission to payment posting.
📞 Book a free consultation today to learn how MedStates can simplify your billing workflow and help your practice stay compliant, profitable, and audit-ready.
 Using the wrong POS can cause underpayment or
Using the wrong POS can cause underpayment or 

